Review: Course and Sections (why splits), Course and Prerequisites (Two entities or one?), Grade (where to store it), minimum grade required for prerequisites
Lecture 1: Forward Engineering: ERD to Relational Model: (Remember these rules, Chapter 6 of LIU)
- Each entity set is converted into a table with its attributes as the columns of the table
- Depending on the mapping cardinality, you modify the tables to make them related
- If the relationship is 1:m or m:1, you put the primary key of the table for one-side entity set into the table for the many-side entity set
- If the relationship is m:m, you build a junction table which has the primary keys of both entity sets as columns
- If the relationship is 1:1, you can put the primary key of one entity set into the table for another entity set.
- Foreign keys are optional if and only the receiving side is optional. Foreign keys in a junction table is always required.
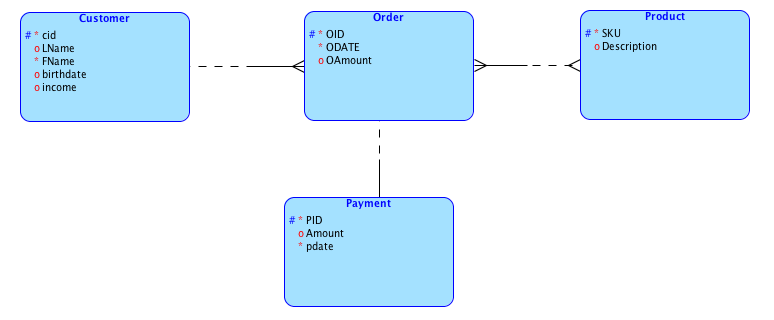
Example 1: Convert the ERD for Customer – Order – Product problem into the relational model
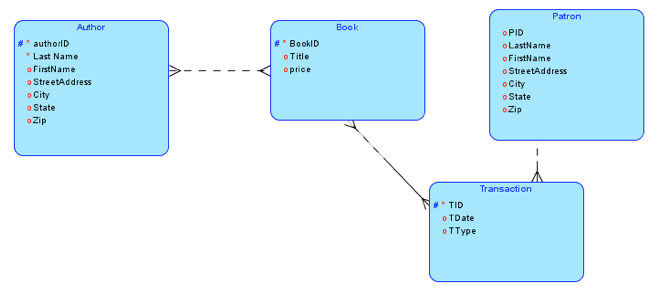
Additional Transformation Exercises:
-
Transform the following E-R diagram into a relational model. Then create the database using Oracle.
- The following relational model was converted from an ERD that has been lost (Bold fields indicate the primary key). Please recover the ERD based on all the information given:
Part: PartNo, Description, Quantity, UnitPrice
Bin: BINNO, Capacity, Location, PartNo
Department: Name, Phone, Contact, Account, Balance
Dept_Part: Department, Part
Supplier: Name, Address, City, State, Zip, Phone
SPL_Part: FK_Name, FK_Partno
Lecture 2: Convert ERD into relational models: conversion rules on Weak entities, gerunds, exclusive relationships, recursive relationships, and super/sub type entities (Chapter 6 of Liu)
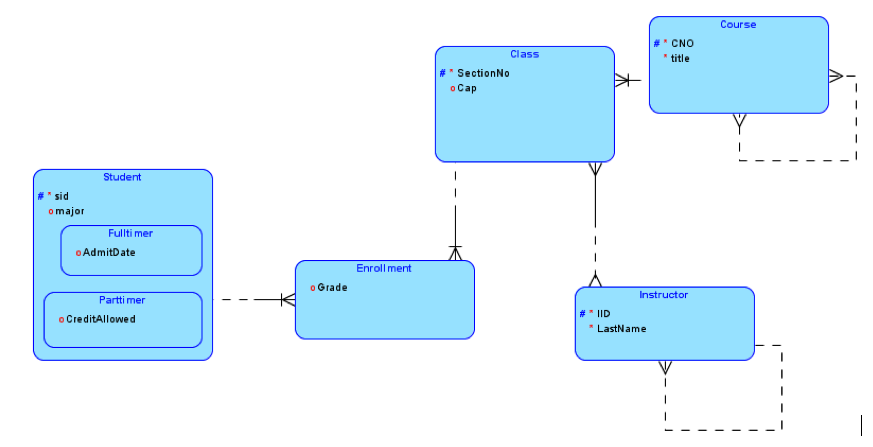
Example 2: Convert the ERD involving courses, perquisites, classes, instructors, and students, and enrollment into a relational model.
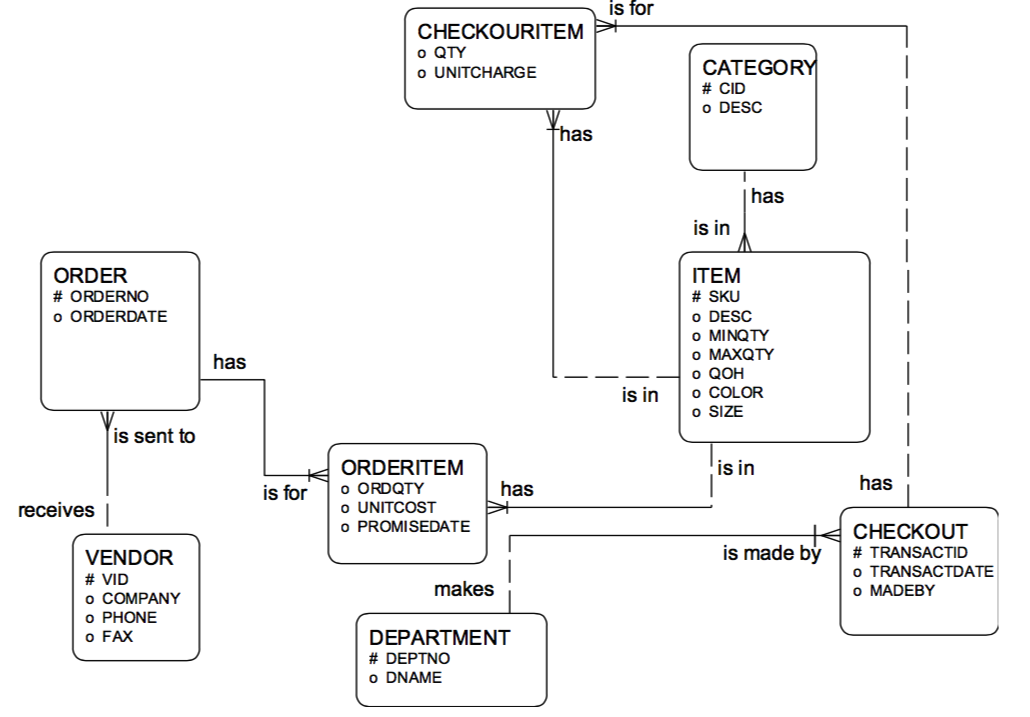
Additional Conversion Examples: Convert the following ERD into a relational model:
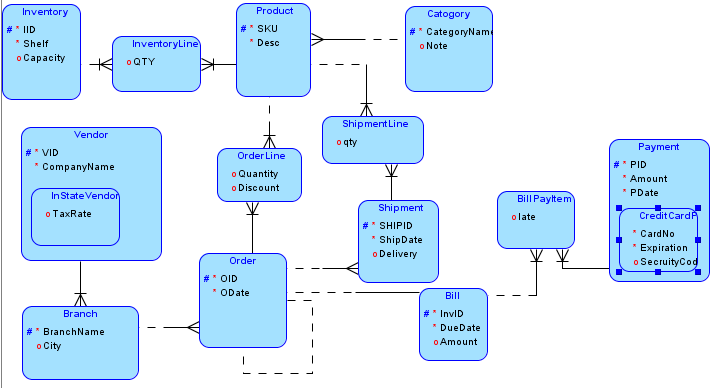
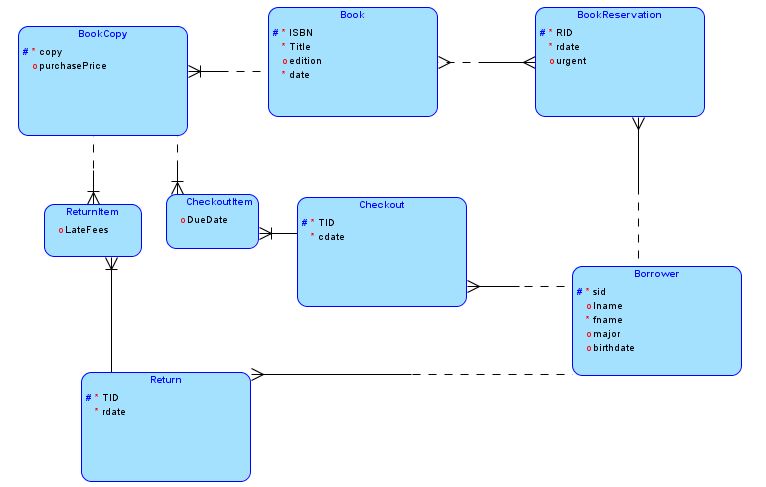 

Reading Assignments: Chapters 3 and 6 of LIU
Writing Assignments:
- Correctness Questions: online at course.org
- Hands-on Questions:
- Convert the following ERD into relational model manually on paper:

|